Old Tom had four sons. He wanted them(learn) not to judge things too quickly. So he sent them to look at an apple tree in different seasons. The first son went in winter, the second in spring, the third in summer, and the youngest in autumn. When they all came back, he called them together to describethey had seen. The sons had different(opinion). Tom then told them that they shouldn't judge a tree, or a person, by only one season.
Everyone(love) snow. But when school stays open despite the snow, it can be really annoying. However, there is one upside of going to schoola cold winter day: you might be smarter. So far, researchers who study the brain(find) that cold temperatures make us think more quickly since messages travel faster among our brain cells. So the scientists say(hang) out on a cold morning may boost the result of any test that day.
A black hole is a spot in space that has(power) gravity. Its gravity is so strong that it pulls everything nearby into it, stars, planets and other things. Black holes form when a star dies. When that happens, a huge amount of matter crowds into a very small space,becomes very dense. Black holes(talk) about in 1783 first. That year, one scientist said that in the universe, there might be places with strong gravity to trap light, although he didn't use the term "black hole".
My Perfect Imperfect Life
A few years ago, I was standing at the barre (扶手杠) waiting for my adult ballet class when I heard a voice behind me. "So, do you have this perfect life?"
My first reaction was to1who was being asked such an odd question. Then I remembered there were only two of us in the room. When I turned2, the other woman was looking straight at me.
I had no idea how to answer it. Was she3? Who has a perfect life? Sure, occasionally I did find the perfect dress or the perfect pair of shoes,4never would I use that word to describe anything about me or my life. I felt a twinge of guilt for somehow giving her that5.
She watched me. I finally6to whisper a quick "No".
By then, the teacher had entered the room and turned on the music to start class. With a sigh of7, I moved my feet into the best position. But as soon as my knees bent for our first pose, I realized my8had been disturbed. This woman's words wouldn't9echoing in my thoughts.
I wanted to know how she came up with her very mistaken10. If she knew anything about my life, she never would have had the11to ask me that question.
I did my best to do our floor exercises in front of the mirror. For a few moments, I didn't see the usual12of my older self attempting to use a beautiful art form to 13my gracefulness. I only saw the little girl whose father died when she was two, the child who walked home from elementary school every day to an empty house, who learned to sew her own clothes to14money.
Perfect. My life had been far from it.
When those memories15, I was left with a vision of the woman I had become, the woman16by all those things I considered imperfect. I now saw the woman who had learned to be self-reliant, who17her family and her friends, who didn't take life for granted. Was that the "perfect" this woman had detected?
I still don't know, but I no longer feel18or feel like I must keep track of all the difficult times to prove my life isn't19. If ever again asked whether my life is perfect, I would have a different20. Because now I see that, despite all its imperfection, it is.
Ray Tokuda, a 54-year-old Japanese American, is proud of the title his school has given him. He is a Shifu, a Chinese word literally meaning a master, mentor or senior practioner of martial arts.

Tokuda has reason to be proud. He has been involved with Chinese martial arts for almost four decades. After learning them at the martial arts school in New Mexico State, today he is among the most experienced kung fu teachers of the school.
Practicing martial arts two to three hours and helping students improve their skills have become Tokuda's daily routine. He expects to practice and teach martial arts for the rest of his life. "I'm still learning. It's worth more than a lifetime to learn Chinese martial arts," he said. "Once I started, I just couldn't stop. I think it's also the magic of Chinese culture."
Tokuda was sent to the martial arts school when he was 10. He still remembers how unwilling he was when starting out. "My father had always wanted to learn Chinese martial arts but never got the chance, so he put his kid in," he said. "I was so afraid at that time because I thought kung fu was all about fighting."
But things changed after he learned that martial arts were more than punching and kicking.
"One of the things martial arts teach me is overcoming adversity," Tokuda said. "As a little kid, my first lesson was like, oh, look, this is a thing that I can get through by diligence, perseverance(毅力)and dedication, and that was priceless for my life."
Learning Chinese martial arts opened a gateway for him to better understand Chinese culture because he could hear a lot of ancient Chinese kung fu-related stories. "It is like in America, where we hear stories about knights in shining armor and King Arthur and noble deeds done," he said. "I feel martial arts preserve something of ancient China that can't be found in books. They are sort of an oral history."
Tokuda has also been invited to various events in his home state to showcase traditional Chinese culture, including the dragon dance and lion dance, which he also learnt at the martial arts school. Because of this, he is now considered a cultural envoy (使者) in the eyes of the public.
New App Helps People Remember Faces
Large gatherings such as weddings and conferences can be socially overwhelming. Pressure to learn people's names only adds to the stress. A new facial-recognition app could come to the rescue, but privacy experts recommend proceeding with caution.

The app, called SocialRecall, connects names with faces via smartphone cameras and facial recognition, potentially avoiding the need for formal introductions. "It breaks down these social barriers we all have when meeting somebody," says Barry Sandrew, who created the app and tested it at an event attended by about 1,000 people.
After receiving an invitation to download SocialRecall from an event organizer, the user is asked to take two selfies and sign in via social media. At the event, the app is active within a previously defined geographical area. When a user points his or her phone camera at an attendee's face, the app identifies the individual, displays the person's name, and links to his or her social media profile. To protect privacy, it recognizes only those who have agreed to participate. And the app's creators say it automatically deletes users' data after an event.
Ann Cavoukian, a privacy expert who runs the Privacy by Design Center of Excellence praises the app's creators for these protective measures. She cautions, however, that when people choose to share their personal information with the app, they should know that "there may be unintended consequences down the road with that information being used in another context that might come back to bite you."
The start-up has also developed a version of the app for individuals who suffer from prosopagnosia, or "face blindness," a condition that prevents people from recognizing individuals they have met. To use this app, a person first acquires an image of someone's face, from either the smartphone's camera or a photograph, and then tags it with a name. When the camera spots that same face in real life, the previously entered information is displayed. The collected data are stored only on a user's phone, according to the team behind the app.
GOING TO UNIVERSITY is supposed to be a mind-broadening experience. That statement is probably made in comparison to training for work straight after school, which might not be so encouraging. But is it actually true? Jessika Golle of the University of Tübingen, in Germany, thought she would try to find out. Her result, however, is not quite what might be expected. As she reports in Psychological Science this week, she found that those who have been to university do indeed seem to leave with broader and more inquiring minds than those who have spent their immediate post-school years in vocational (职业的) training for work. However, it was not the case that university broadened minds. Rather, work seemed to narrow them.
Dr. Golle came to this conclusion after she and a team of colleagues studied the early careers of 2,095 German youngsters. The team used two standardized tests to assess their volunteers. One was of personality traits, including openness, conscientiousness(认真)and so on. The other was of attitudes, such as realistic, investigative and enterprising. They administered both tests twice—once towards the end of each volunteer's time at school, and then again six years later. Of the original group, 382 were on the intermediate track, from which there was a choice between the academic and vocational routes, and it was on these that the researchers focused. University beckoned for 212 of them. The remaining 170 chose vocational training and a job.
When it came to the second round of tests, Dr. Golle found that the personalities of those who had gone to university had not changed significantly. Those who had undergone vocational training and then got jobs were not that much changed in personality, either—except in one crucial respect. They had become more conscientious.
That sounds like a good thing, certainly compared with the common public image of undergraduates as a bunch of lazybones. But changes in attitude that the researchers recorded were rather worrying. In the university group, again, none were detectable. But those who had chosen the vocational route showed marked drops in interest in tasks that are investigative and enterprising in nature. And that might restrict their choice of careers.
Some investigative and enterprising jobs, such as scientific research, are, indeed beyond the degreeless. But many, particularly in Germany, with its tradition of vocational training, are not. The researchers mention, for example, computer programmers and finance-sector workers as careers requiring these traits. If Dr. Golle is correct, and changes in attitude brought about by the very training Germany prides itself on are narrowing people's choices, that is indeed a matter worthy of serious consideration.
Smile! It makes everyone in the room feel better because they, consciously or unconsciously, are smiling with you. Growing evidence shows that an instinct for facial mimicry(模仿) allows us to empathize with and even experience other people's feelings. If we can't mirror another person's face, it limits our ability to read and properly react to their expressions. A review of this emotional mirroring appears on February 11 in Trends in Cognitive Sciences.
In their paper, Paula Niedenthal and Adrienne Wood, social psychologists at the University of Wisconsin, describe how people in social situations copy others' facial expressions to create emotional responses in themselves. For example, if you're with a friend who looks sad, you might "try on" that sad face yourself without realizing you're doing so. In "trying on" your friend's expression, it helps you to recognize what they're feeling by associating it with times in the past when you made that expression. Humans get this emotional meaning from facial expressions in a matter of only a few hundred milliseconds.
"You reflect on your emotional feelings and then you generate some sort of recognition judgment, and the most important thing that results in is that you take the appropriate action—you approach the person or you avoid the person," Niedenthal says. "Your own emotional reaction to the face changes your perception of how you see the face in such a way that provides you with more information about what it means."
A person's ability to recognize and "share" others' emotions can be prevented when they can't mimic faces. This is a common complaint for people with motor diseases, like facial paralysis(瘫痪) from a stroke, or even due to nerve damage from plastic surgery. Niedenthal notes that the same would not be true for people who suffer from paralysis from birth, because if you've never had the ability to mimic facial expressions, you will have developed compensatory ways of interpreting emotions.
People with social disorders associated with mimicry or emotion-recognition damage, like autism(自闭症), can experience similar challenges. "There are some symptoms in autism where lack of facial mimicry may in part be due to limitation of eye contact," Niedenthal says.
Niedenthal next wants to explore what part in the brain is functioning to help with facial expression recognition. A better understanding of that part, she says, will give us a better idea of how to treat related disorders.
Benefits of Sports
Doing sports is a physical, mental and social adventure. It's a great way for children to take a break from academics and release extra energy. It also helps them lead fuller and happier lives as regular sports have proven to improve overall well-being.
The physical benefits of doing sports are probably the most obvious. Regardless of your fitness level when you start playing sports, you'll notice an increase in your overall fitness once you're involved.Basketball players focus on strength training; football players work on speed while track athletes train through longer runs. The training process helps promote physical fitness and performances in competitions.
Playing sports contributes to mental health, helping to increase confidence and self-worth. A pat on the back, high-five from a teammate, or handshake after a match really boosts a child's confidence. Words of praise and encouragement from the coach, parents and other players raise the self-worth.So after a game, it's a better idea to ask "Did you enjoy the game?" rather than "Did you win?"
Children who participate in sports might also benefit from the social aspect, feeling part of a group, building up accountability and leadership.Teamwork involves both being dependable as a teammate and learning to rely on your teammates to achieve a positive outcome. Teamwork breeds accountability and challenges you to be responsible for your actions. Being part of a team gives you an opportunity to be a leader.
Discipline is another social advantage. Most organized sports require a strict training and practice schedule. As a student-athlete, you need to balance academics and athletics.
There is no shortage of reasons to find a sport to get involved in. Are you ready to go? Pick one and get moving!
A. It's not just your body that benefits from sports.
B. Therefore, playing sports is going to make you more fit.
C. But remember, a child's self-worth should not be distinguished by victory or loss.
D. If you play group sports, you'll be part of a team that takes direction from a coach.
E. Nearly every sport requires physical activity and the skills needed to be competitive.
F. Among these, learning how to function as part of a team is the most important advantage.
G. Only with strict discipline can you be successful both in the classroom and in the sports field.
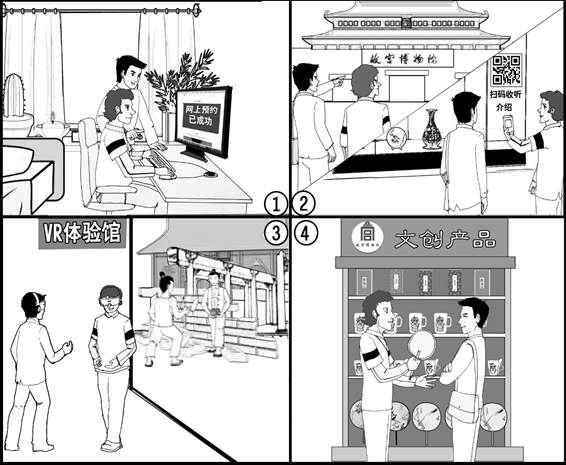
1)推荐曲目;
2)推荐理由;
3)你的祝愿。
注意: 1)词数不少于50;2)开头和结尾已给出,不计入总词数。
Dear Jim,
Yours,
Li Hua
注意:词数不少于60。
提示词:二维码 QR code